What is a heat exchanger?
A heat exchanger is a device that can transfer heat from one medium to another. A common type of heat exchanger is a car radiator, which transfer heat from hot water (engine coolant) into the air that is passed through the radiator.
What is a wood stove heat exchanger?
An air to air heat exchanger installed in the flue of a wood stove is warmed by the exiting hot air rising in the flue, which heats the tubes inside the heat exchanger. The heat is then extracted by blowing cooler air through the heat
exchanger tubes.
The most common type of slow combustion wood stove heat exchanger is installed in the flue. Hot air from the fire is drawn up the flue and although the flue will become warm, much of the heat within is lost to the atmosphere where the flue terminates. A lot of the heat exiting the flue is reclaimable with a flue mounted heat exchanger. A heat exchanger installed in the flue is warmed by the hot air rising in the flue which is then extracted by either radiation or blowing cooler air through the heat exchanger.
There are other types of wood fire place heat exchangers, including grates and plates that we won’t cover in this article. These fire place type heat exchangers will usually rely on the thermal mass of these devices being heated by the fire, the thermal mass then radiates heat in all directions instead of being lost up the chimney.
How does a flue mounted wood stove heat exchanger work?
Designs of flue mounted wood stove heat exchangers will vary, but the principle of all designs is the same.
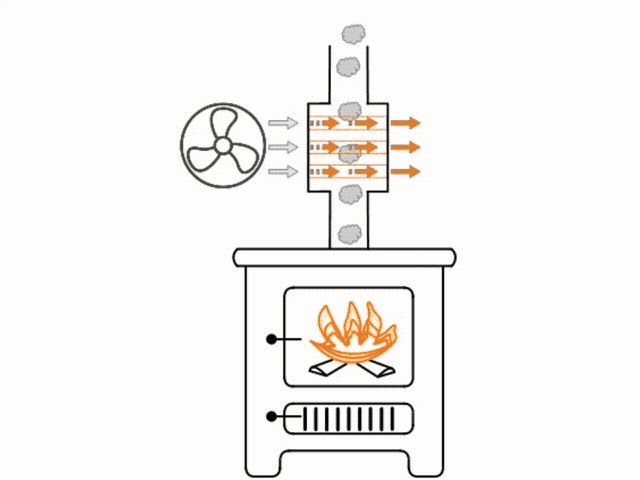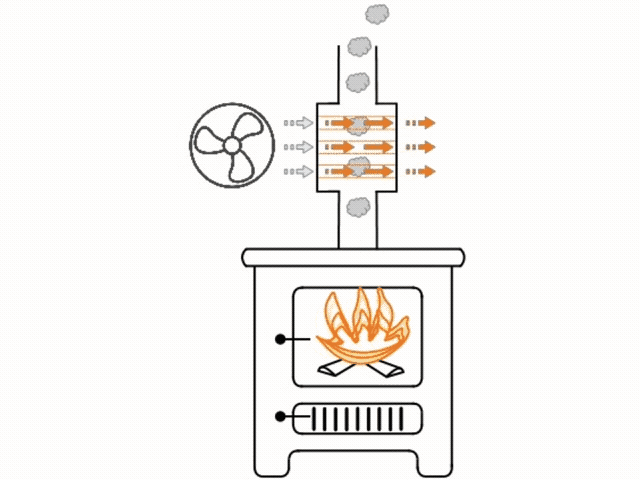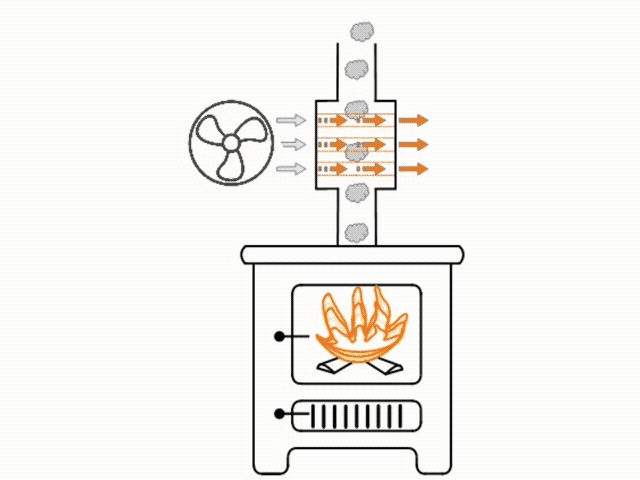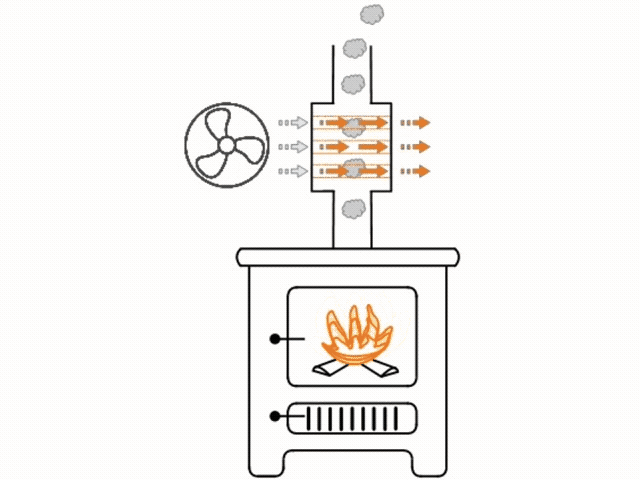
The heat exchanger is installed in line with the flue. All of the hot air being drawn up the flue from the fire passes through the heat exchanger. Inside the heat exchanger are either sealed coils or straight pieces of tube. The inside of the coils or tube are hollow and exposed to the room atmosphere.
The outside of the coils or tube are heated as they are exposed to the hot air rising in the flue. As the tubes warm, a fan will blow room air through the tubes, quickly heating that air, before it exits the tubes and circulates into the room. As the coils or tube are air tight sealed, smoke from within the flue cannot transfer to the inside of the coils or tube.
Blowing air through the tubes helps to keep a temperature difference in the tube, therefore increasing radiation and making the heat exchanger more efficient.
This video of a double barrel wood stove heat exchanger gives a good insight as to how flue mounted heat exchangers work.
How does a wood stove heat exchanger save money and keep me warmer?
Consider a wood stove (without a heat exchanger installed) burning wood in a room. Given a certain amount of wood and air the fire will heat the wood stove to a certain temperature and radiate a certain amount of heat into the room. Hot air generated from the fire is drawn up the flue and out to the atmosphere.
When a heat exchanger is installed in the flue that (previously wasted) hot air warms the heat exchanger which is used to deliver more heat into the room.
This situation provides an opportunity to either, produce more heat from the same size fire, create a smaller fire to produce the same amount of heat, or some combination of more heat and smaller fire.
As the price of firewood continues to escalate the payback time on a heat exchanger by saving the amount of wood burnt is relatively quick.